Evaluating Conditions:
Comparison Operations:
You can evaluate a situation by comparing one value in the script to what you expect it might be. The result will be a boolean: True or False.
- == Is Equal To: This operator compares two values to see if they are the same.
- ‘Hello’ = ‘Hi’ returns FALSE because they aren’t the same string.
- != Is Not Equal To: This operator compares two values to see if they are not the same.
- ‘Hello’ = ‘Hi’ returns TRUE because they are the same string.
- === Strict Equal To: This operator compares two values to check that both the data type and the value are the same.
- !== Strict Not Equal To: This operator compares two values to check that both the data type and the value aren’t the same.
- > Greater Than: This operator checks if the number on the left is greater than the number on the right.
- < Less Than: This operator checks if the number on the left is less than the number on the right.
- >= Greater Than Or Equal To: This operator checks if the number on the left is greater than or equal to the number on the right.
- <= Less Than Or Equal To: This operator checks if the number on the left is less than or equal to the number on the right.

Logical Operators:
Comparison Operators usually return single values of true or false. Logical Operators allow you to compare the results of more than one comparison operator.
Logical Operatore types:
- && Logical AND: This operator tests more than one condition. If both expressions evaluate to true, then the expression results true. If just one of these returns false, then the expression will return false.
-
** Logical Or**: This operator tests at least one condition. If either expression evaluates to true, then the expression results true. If just both return false, then the expression will return false. - ! Logical Not: This operator takes a single Boolean value and inverts it. This reverses the state of an expression.
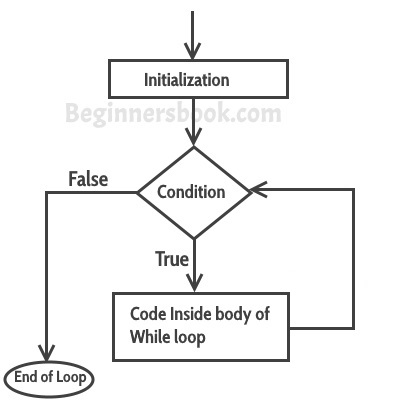
LOOPS:
LOOPS check a condition. If itreturns true, a code block will run. Then the condition will be checked again and if it still returns true, the code block will run again. It repeats until the condition returns false.
Loops types:
- FOR: Used to run a code a specific number of times. In a for loop, the condition is usually a counter which is used to tell how many times the loop should run.
- WHILE: Used when you don’t know how many times the code should run. Here the condition can be something other than a counter, and the code will continue to loop for as long as the condition is true.
- DO WHILE: It’s very similar to the While loop, but has one key difference: it will always run the statements inside the curly braces at least once, even if the condition evaluates to false.