HTMLs: Forms
HTML borrows the concept of a form to refer to different elements that allow you to collect information from visitors to your site. Whether you are adding a simple search box to your website or you need to create more complicated insurance applications, HTML forms give you a set of elements to collect data from your users.
Why Forms?
In addition to enabling users to search, forms also allow users to perform other functions online. You will see forms when registering as a member of a website, when shopping online, and when signing up for newsletters or mailing lists.

Form Controls
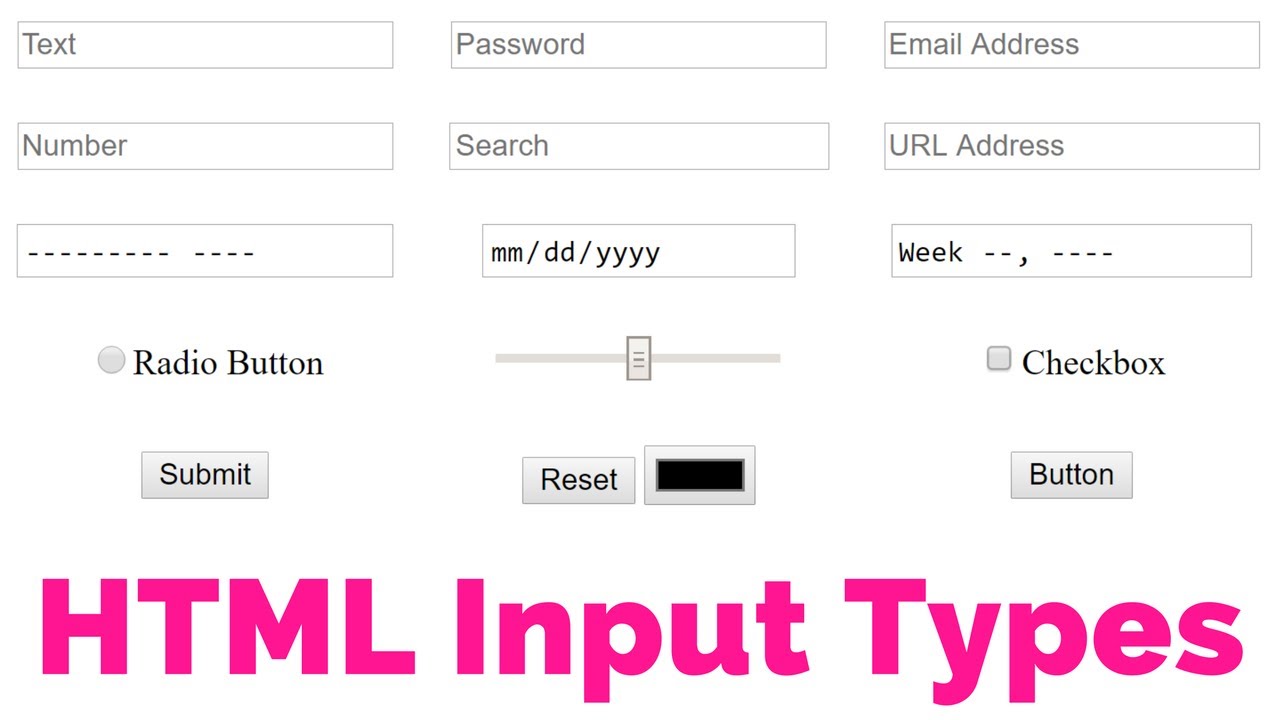
- ADDING TEXT:
- Text input (single-line): Used for a single line of text such as email addresses and names.
- Password input: Like a single line text box but it masks the characters entered.
- Text area (multi-line): For longer areas of text, such as messages and comments.
- Making Choices:
- Radio buttons: For use when a user must select one of a number of options.
- Checkboxes: When a user can select and unselect one or more options.
- Drop-down boxes: When a user must pick one of a number of options from a list.
- Submitting Forms:
- Submit buttons: To submit data from your form to another web page.
- Image buttons: Similar to submit buttons but they allow you to use an image.
- Uploading Files:
- File upload: Allows users to upload files (e.g. images) to a website.
How Forms Work
- A user fills in a form and then presses a button to submit the information to the server.
- The name of each form control is sent to the server along with the value the user enters or selects.
- The server processes the information using a programming language such as PHP, C#, VB.net, or Java. It may also store the information in a database.
- The server creates a new page to send back to the browser based on the information received.
To differentiate between various pieces of inputted data, information is sent from the browser to the server using name/value pairs. If the form control allows the user to enter text, then the value of the form control is whatever the user has typed in. If the form control allows you to choose from a fixed set of answers, the web page author will add code that gives each option an automatic value.
Form Structure
- form: Form controls live inside a (form) element. This element should always carry the action attribute and will usually have a method and id attribute too.
- action: Every (form) element requires an action attribute. Its value is the URL for the page on the server that will receive the information in the form when it is submitted.
- method: Forms can be sent using one of two methods: get or post. With the get method, the values from the form are added to the end of the URL specified in the action attribute. With the post method the values are sent in what are known as HTTP headers.
- id: The value is used to identify the form distinctly from other elements on the page.
Labelling Form Controls
(label): When introducing form controls, the code was kept simple by indicating the purpose of each one in text next to it. However, each form control should have its own (label) element as this makes the form accessible to vision-impaired users. This element can be used in two ways. It can:
- Wrap around both the text description and the form input.
- Be kept separate from the form control and use the for attribute to indicate which form control it is a label for.
Grouping Form Elements
- (fieldset) You can group related form controls together inside the (fieldset) element. This is particularly helpful for longer forms.
- (legend) The (legend) element can come directly after the opening (fieldset) tag and contains a caption which helps identify the purpose of that group of form controls.
HTML5: Form Validation
You have probably seen forms on the web that give users messages if the form control has not been filled in correctly; this is known as form validation. Validation helps ensure the user enters information in a form that the server will be able to understand when the form is submitted.
HTML5: Date Input
- (input): Many forms need to gather information such as dates, email addresses, and URLs. This has traditionally been done using text inputs.
- type=”date”: If you are asking the user for a date, you can use an (input) element and give the type attribute a value of date. This will create a date input in browsers that support the new HMTL5 input types.
HTML5: Email & URL Input
- (input) HTML5 has also introduced inputs that allow visitors to enter email addresses and URLs. Browsers that do not support these input types will just treat them as text boxes.
- type=”email”: If you ask a user for an email address, you can use the email input.
- type=”url”: A URL input can be used when you are asking a user for a web page address.
HTML5: Search Input
- (input): If you want to create a single line text box for search queries, HTML5 provides a special type of input for that purpose.
- type=”search”: If you want to create a single line text box for search queries, HTML5 provides a special search input.
CSS: Lists, Tables and Forms
Bullet Point Styles: list-style-type
The list-style-type property allows you to control the shape or style of a bullet point (also known as a marker). It can be used on rules that apply to the (ol), (ul), and (li) elements.
Images for Bullets: list-style-image
You can specify an image to act as a bullet point using the list-style-image property. The value starts with the letters url and is followed by a pair of parentheses. Inside the parentheses, the path to the image is given inside double quotes.
Positioning the Marker: list-style-position
Lists are indented into the page by default and the list-styleposition property indicates whether the marker should appear on the inside or the outside of the box containing the main points.
List Shorthand: list-style
As with several of the other CSS properties, there is a property that acts as a shorthand for list styles. It is called list-style, and it allows you to express the markers’ style, image and position properties in any order.
Table Properties
Border on Empty Cells: empty-cells
- show: This shows the borders of any empty cells.
- hide: This hides the borders of any empty cells.
- inherit: If you have one table nested inside another, the inherit value instructs the table cells to obey the rules of the containing table.
Gaps Between Cells: border-spacing, border-collapse
- The border-spacing property: allows you to control the distance between adjacent cells.
- collapse Borders: are collapsed into a single border where possible. (border-spacing will be ignored and cells pushed together, and empty-cells properties will be ignored.)
- separate Borders: are detached from each other. (border-spacing and empty-cells will be obeyed.)
Styling Forms
Styling Text Inputs
- font-size sets the size of the text entered by the user.
- color sets the text color, and background-color sets the background color of the input.
- border adds a border around the edge of the input box, and border-radius can be used to create rounded corners (for browsers that support this property).
- The :focus pseudo-class is used to change the background color of the text input when it is being used, and the :hover psuedo-class applies the same styles when the user hovers over them.
- background-image adds a background image to the box.
Styling Submit Buttons
- color is used to change the color of the text on the button.
- text-shadow can give a 3D look to the text in browsers that support this property.
- border-bottom has been used to make the bottom border of the button slightly thicker, which gives it a more 3D feel.
- background-color can make the submit button stand out from other items around it.
- The :hover pseudo-class has been used to change the appearance of the button when the user hovers over it.
cursor Styles
The cursor property allows you to control the type of mouse cursor that should be displayed to users. Here are the most commonly used values for this property:
auto
crosshair
default
pointer
move
text
wait
help
url(“cursor.gif”);
